44 coupon vs interest rate
Important Differences Between Coupon and Yield to Maturity Keep in mind that the coupon is always 2% ($20 divided by $1,000). That doesn't change, and the bond will always payout that same $20 per year. But when the price falls from $1,000 to $500, the $20 payout becomes a 4% yield ($20 divided by $500 gives us 4%). Bond Basics: How Interest Rates Affect Bond Yields ... Once issued, the coupon never changes - but prevailing interest rates can. When that happens, an existing bond's coupon rate may become more or less attractive by comparison, and that affects its price. When an existing bond has a higher coupon than a newly issued bond, it pays out more income.
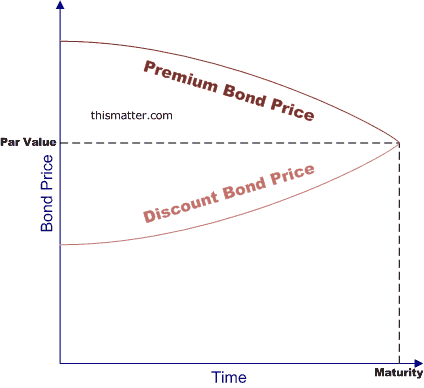
Premium vs Discount Bonds: Which Should You Buy? - SmartAsset Coupon rate; Bond ratings; When deciding whether to invest in bonds, it's also important to look at the bigger picture to determine whether it's a good fit for your investment strategy. Keeping the interest rate environment in focus can also help you to gauge which way bond prices are likely to move, at least in the near term.
Coupon vs interest rate
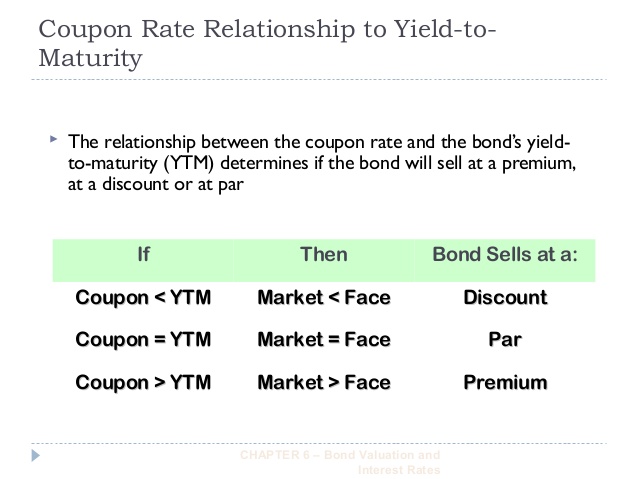
What's the Difference Between Premium Bonds and Discount ... What Makes Them Different? A premium bond has a coupon rate higher than the prevailing interest rate for that bond maturity and credit quality. A discount bond, in contrast, has a coupon rate lower than the prevailing interest rate for that bond maturity and credit quality. An example may clarify this distinction. APR vs. Interest Rate: How are They Different? The fees turn the interest rate into an APR of 3.37%. Loan B, which has an interest rate of 3%, 1 discount point costing $2,000, and $3,000 in other lender fees. The point and other fees turn the interest rate into an APR of 3.20%. Interest rates between the two loans differ by a quarter point (0.25). Difference Between Coupon Rate and Interest Rate (With ... Main Differences Between Coupon Rate and Interest Rate Coupon rates are calculated on the fixed-income security, whereas interest rates are calculated on the amount which has been lent to borrowers. The coupon's face value determines the nominal value of the bond. Albeit the Interest rate's face value affected by the amount due on.
Coupon vs interest rate. Premium vs. Discount Bonds: What's the Difference ... For example, a $500 bond that trades for $525 is a premium bond. This happens when the bond's coupon rate exceeds the prevailing interest rate. So, for example, the prevailing interest rate might be 4%, while the bond's coupon rate is 6%. This superior coupon rate is why the bond trades at a premium in secondary markets. APY vs Interest Rate: What Is the Difference [Guide for 2022] The main difference between APY and interest rate is the compounding interest. An APR or simple interest is usually distinguished in the context of borrowed money, while the APY is more commonly associated with the interest you gain when you invest money. Simple interest rates can be applied to both borrowing and investing money. Prime Rate - Current Prime Rate and Federal Funds Rate The current prime rate among major U.S. banks is 3.5%. The rate rose this week for the first time since 2020 after the Federal Reserve increased its key benchmark rate by a quarter-point to try to quell inflation. The prime rate runs 3 percentage points above the central bank's federal funds rate, which the Fed just raised to a target range ... Understanding Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity of Bonds ... The Coupon Rate is the amount that you, as an investor, can expect as income as you hold the bond. The coupon rate for each bond is fixed upon issuance. Here's a sample computation for a Retail Treasury Bond issued by the Bureau of Treasury: The Coupon Rate is the interest rate that the bond pays annually, gross of applicable taxes.
Interest Rates | Chart Pack | RBA Policy Interest Rates. Australian Cash Rate and 90-day Bill Yield. Policy Interest Rates - Selected Advanced Economies. Monetary Policy - China. 10-year Australian Government Bond Yield. Policy Interest Rates - Emerging Markets. 10-year Government Bond Yields. Spread between Australian 10-year Bond Yield and the Cash Rate. Interest rates are rising. Here's what to do if you're ... A simplified way to think about why bond prices fall when rates rise is this: All else being equal, if someone could buy a 10-year bond paying 1.5% interest a year or a shorter-term bond that pays ... 4 Best Low-Interest Personal Loans of 2022 | ConsumerAffairs The interest rate is the cost of borrowing money from a lender. It's expressed as an annual percentage of the loan amount borrowed. Each month, a portion of your payment will go toward interest,... APY: Definition, Formula, How It's Calculated To get a better sense of how APY works, let's take an example. Here's the formula for APY: Alex Ford/Insider. Let's say, for example, you deposit $1,000 into a 12-month CD offering a 5% APY ...
The Difference Between Interest Rate & Yield to Maturity ... The interest that the investor is paid is referred to as a coupon rate. The interest rate paid is based on the principal amount of the debt instrument. The interest is paid periodically. A security's coupon rate might be real, nominal or effective, so the income an investor receives by holding a fixed income security will vary. A nominal rate ... Stated interest rate definition - AccountingTools The stated interest rate is the interest rate listed on a bond coupon. This is the actual amount of interest paid by the bond issuer. Thus, if the issuer pays $60 on a bond with a face value of $1,000, then the stated interest rate is 6%. Basics Of Bonds - Maturity, Coupons And Yield Say you invest $5,000 in a six-year bond paying a coupon rate of five percent per year, semi-annually. Assuming you hold the bond to maturity, you will receive 12 coupon payments of $125 each, or a total of $1,500. Accrued interest is the interest that adds up (accrues) each day between coupon payments. APR vs. interest rate: What are the differences? - CNET Interest paid at 3.50%: $184,968.26 Though the numbers may be smaller for a credit card or car loan, modest differences in interest rates can add up over the years. Other costs In addition to your...
Credit cards, interest rates and APRs: Everything you need ... According to LendingTree, the average credit card balance in early 2021 was $6,569. If you had a credit card APR of 16% and only made the minimum payments, you could pay more than $8,200 in ...
Yield to Maturity vs. Coupon Rate: What's the Difference? To calculate the bond's coupon rate, divide the total annual interest payments by the face value. In this case, the total annual interest payment equals $10 x 2 = $20. The annual coupon rate for...
Interest Vs. Dividends: Definition, Pros & Cons Investing $1,000 in a one-year CD at a rate of 3% would yield $30 in simple interest over the term, plus your initial $1,000 investment. Not the greatest return, but it's guaranteed.
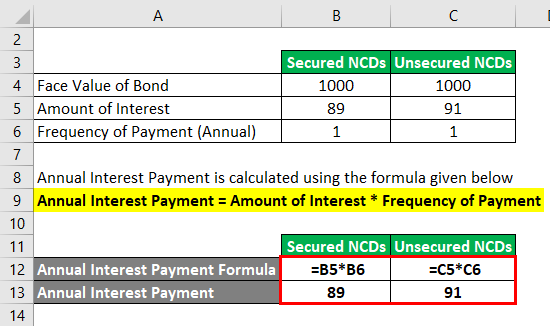
Difference Between Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity (With ... The coupon rate represents the annual interest payments that will be received by the issuer of the bond. The coupon rate can be measure with the simple mathematical formula by dividing the annual payment by the face value of the bond multiplied by 100. This formula can be deduced as follows: Coupon Rate = Annual Payment / Face Value × 100
Bond ETFs and rising rates finally explained ... In a pessimistic scenario, over a 2x duration period * the increased rates dragging the ETF price down will be fully offset by newly issued Bonds' higher coupons. In a nutshell, the longer the duration of the ETF, the more pain you have to endure. This is because you are taking more risk and earning potentially more return.
Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities | TIPS: Perfect ... The combination of the fixed rate and inflation-adjusted rate creates the I Bonds' composite interest rate, which was 7.12% but now rises to 9.62%, the highest in history for I Bonds. An I Bond bought today will earn 9.62% (annualized) for six months and then get a new composite rate every six months for its 30-year term.
Coupon Rate Calculator | Bond Coupon For a plain-vanilla bond, the coupon rate of the bond does not change with the market interest rates - it is fixed when the bond is issued.. However, bonds issued in a high-interest rate environment are more likely to have a higher coupon rate. Even when the interest rate goes down, the coupon rate will still stay the same. Hence, a higher coupon rate bond, in general, provides better ...
APR Vs. Interest Rate: Knowing The Difference Can Save You ... Going back to Freddie Mac's Primary Mortgage Market survey, there's an important piece of additional information you need to know: The average interest rate of 2.91% comes with an average of 0.8...
Bond Yield Rate vs. Coupon Rate: What's the Difference? The coupon rate is the interest rate paid by a bond relative to its par or face value. For a fixed-rate bond, this will be the same for its entire maturity. Prevailing interest rates may rise or...
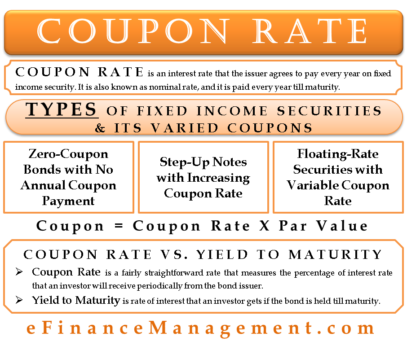
What Is the Coupon Rate of a Bond? A coupon rate is the nominal or stated rate of interest on a fixed income security, like a bond. This is the annual interest rate paid by the bond issuer, based on the bond's face value. These interest payments are usually made semiannually. This article will discuss coupon rates in detail.
Difference Between Coupon Rate and Interest Rate (With ... Main Differences Between Coupon Rate and Interest Rate Coupon rates are calculated on the fixed-income security, whereas interest rates are calculated on the amount which has been lent to borrowers. The coupon's face value determines the nominal value of the bond. Albeit the Interest rate's face value affected by the amount due on.
APR vs. Interest Rate: How are They Different? The fees turn the interest rate into an APR of 3.37%. Loan B, which has an interest rate of 3%, 1 discount point costing $2,000, and $3,000 in other lender fees. The point and other fees turn the interest rate into an APR of 3.20%. Interest rates between the two loans differ by a quarter point (0.25).
What's the Difference Between Premium Bonds and Discount ... What Makes Them Different? A premium bond has a coupon rate higher than the prevailing interest rate for that bond maturity and credit quality. A discount bond, in contrast, has a coupon rate lower than the prevailing interest rate for that bond maturity and credit quality. An example may clarify this distinction.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-02-10d2adc981ea475eb2165a5ec13082ed.jpg)



Post a Comment for "44 coupon vs interest rate"